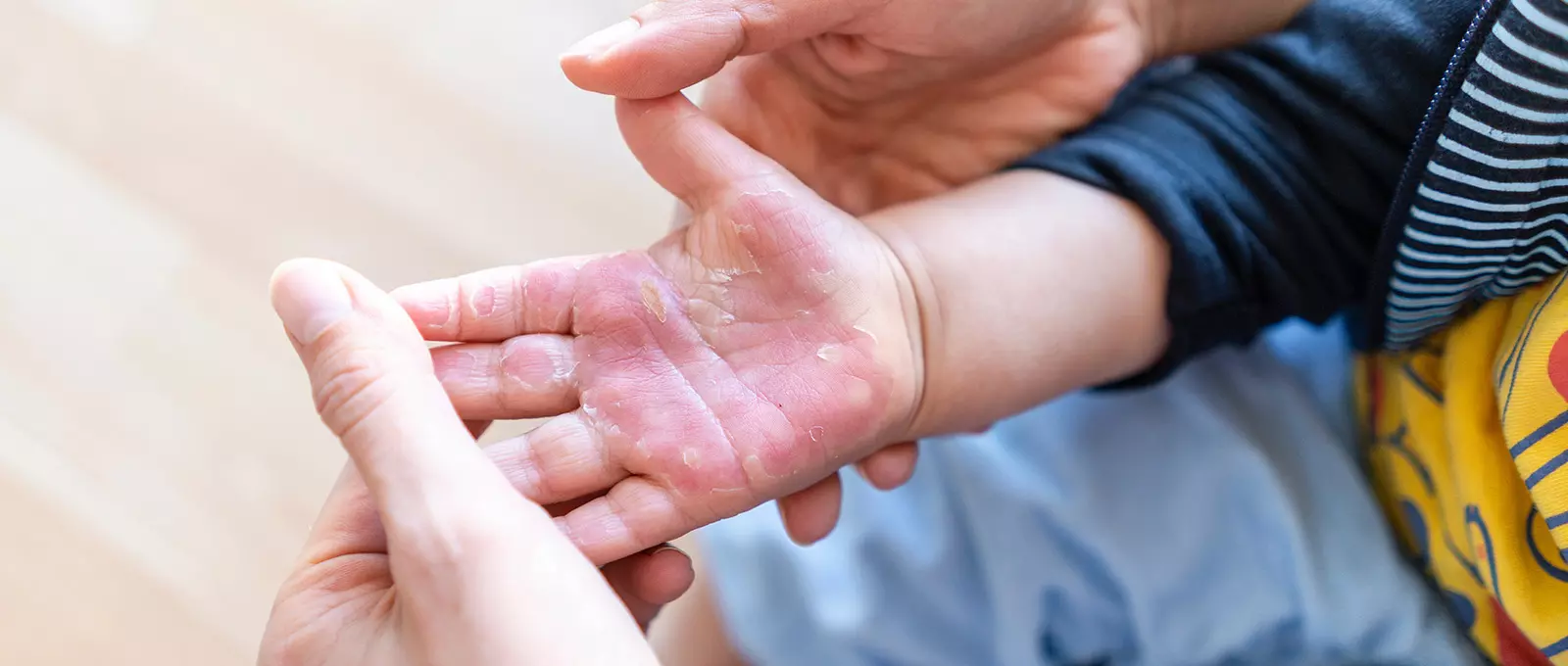
Burns are skin damage that happens due to contact or exposure to extreme heat or other harmful substances. The level of exposure determines the level of damage to the skin, and it can range from mild to moderate to severe. While some mild burns may only require home treatment and resolve after a couple of days, Severe burns can cause permanent scarring, disfiguring, and death.
If you or a loved one has suffered severe burn injuries requiring hospitalization because of a company’s negligence or defective product, contact us to evaluate whether you can recover compensation from those responsible for your injuries.
How Burns Are Classified
Classification of burn injury or burn classifications is made according to the severity and the depth of the tissue damage. Another consideration is the percentage of the total body area that was affected by the burn. The classifications of burn injury depth help healthcare providers determine the appropriate treatment in every case.
First-Degree Burn
First-degree (superficial burns) are the mildest of all burn cases. They affect only the outer layer of the skin, known as the epidermis. A first-degree burn will often cause redness of the skin and a dry and painful burn site but without any blister. A good example of a first-degree burn is a mild sunburn. First-degree burns rarely cause permanent skin damage and generally will heal after a couple of days without any scarring.
Second-Degree Burn
Second-degree (partial thickness)burns affect the epidermis and part of the second skin layer, known as the dermis. This is the most common burn type, and you may be able to treat mild cases at home.
Common signs of a second-degree burn include redness of the skin and blisters. The burn site will also be swollen, painful, and have a moist and shiny appearance. Second-degree burns may lead to an increase in the thickness of the affected skin area.
Third-Degree Burn
Third-degree (full-thickness burns) affect the epidermis, dermis, and fat. The damage also extends to hair follicles and sweat glands. Third-degree burns typically damage nerve endings, so you may not feel pain at the burn site. Rather, you’ll feel pain in the skin area close to the burn site. The skin may appear black, white, or red and have a leathery appearance.
A third-degree burn that affects a limb may impair the mobility of the limb. Generally, third-degree burns will not heal without adequate medical attention, and skin grafting may be necessary.
Fourth-Degree Burn
Fourth-degree burns are the most severe and deepest burn type and can be potentially life-threatening. It affects both layers of skin, the epidermis and dermis, as well as the underlying soft tissues. It can also involve the muscles, tendons, and/or bones. You may see exposed bones and muscle tissue.
Fourth-degree burns may have a charred-looking appearance. And, unlike other burn types, the victim may not feel any pain at all. This is because the nerves responsible for sending pain signals to the brain have been destroyed. However, this doesn’t make it any less serious.
Types of Burns
There are different types of burn classifications based on the source.
- Thermal burn: Thermal burn occurs when your body makes contact with a hot object, such as a hot surface on your cooking stove, hot oil, or hot steam. Most burns that occur in the home are thermal burns, and many of them can be treated at an outpatient clinic or local hospital.
- Radiation burn: This is also known as radiation dermatitis, and it’s a common side effect of radiation therapy. Radiation therapy is a form of treatment used to treat certain cancer types by passing radiation to the target cancer cells. Over time the effect of the radiation on the skin may develop into radiation burns. This burn can also occur from exposure to the sun’s ultraviolet rays and other radiation sources, e.g., x-ray.
- Chemical burns: Chemical burns occur when skin or eyes come into contact with harmful chemicals, such as strong acids or alkalis. People who work in industries that use chemicals, for example, oil rig workers, are more at risk of suffering from chemical burns. Chemical burns are often severe and can cause serious complications.
- Electrical burns: Electrical burns occur when an electric current passes through the body. The extent of injuries depends on the voltage level the body was exposed to. You can treat mild electrical burns like first-degree burns, while serious electrical burns can cause organ damage or even death.
The Types of Burn Injuries
Burns can lead to several temporal and permanent injuries to the victims depending on the source of the heat and the extent of damage caused. Burns can cause various health complications, including the following:
- Bacterial infection that may progress to bloodstream infection (sepsis)
- Breathing difficulties caused by inhaling hot air or smoke
- Fluids loss, including decreased blood volume (hypovolemia)
- Bone and joint issues, such as when scar tissue causes skin, muscles, or tendons to shorten and tighten (contractures)
- Critically low body temperature (hypothermia)
- Scars or ridged regions created by scar tissue overgrowth (keloids)
- Loss of limbs or disfigurement
- Emotional trauma
Let's Discuss Your Burn Injury Claim
Burn injuries can be life-altering. No one deserves to be a victim, especially when it could have been avoided with extra carefulness. If another person’s negligence or defective product caused your permanent burn injury, you may be able to recover compensation for the damages you have suffered. A personal injury lawyer can help you hold those responsible accountable.
The experienced and compassionate personal injury attorneys at Dunn Sheehan LLP are ready to help you with your burn injury claim and help you rebuild your life after a burn accident. Contact us today to see how we can help.